Note: Feel free to reply to this post adding additional info or correcting any inaccuracies on Quantum breakthroughs or the key players discussed.
The tables below provide an overview of the principal companies in the sector—public and private—accompanied by short definitions for clarity, and concluding with a Quantum Architecture summary.
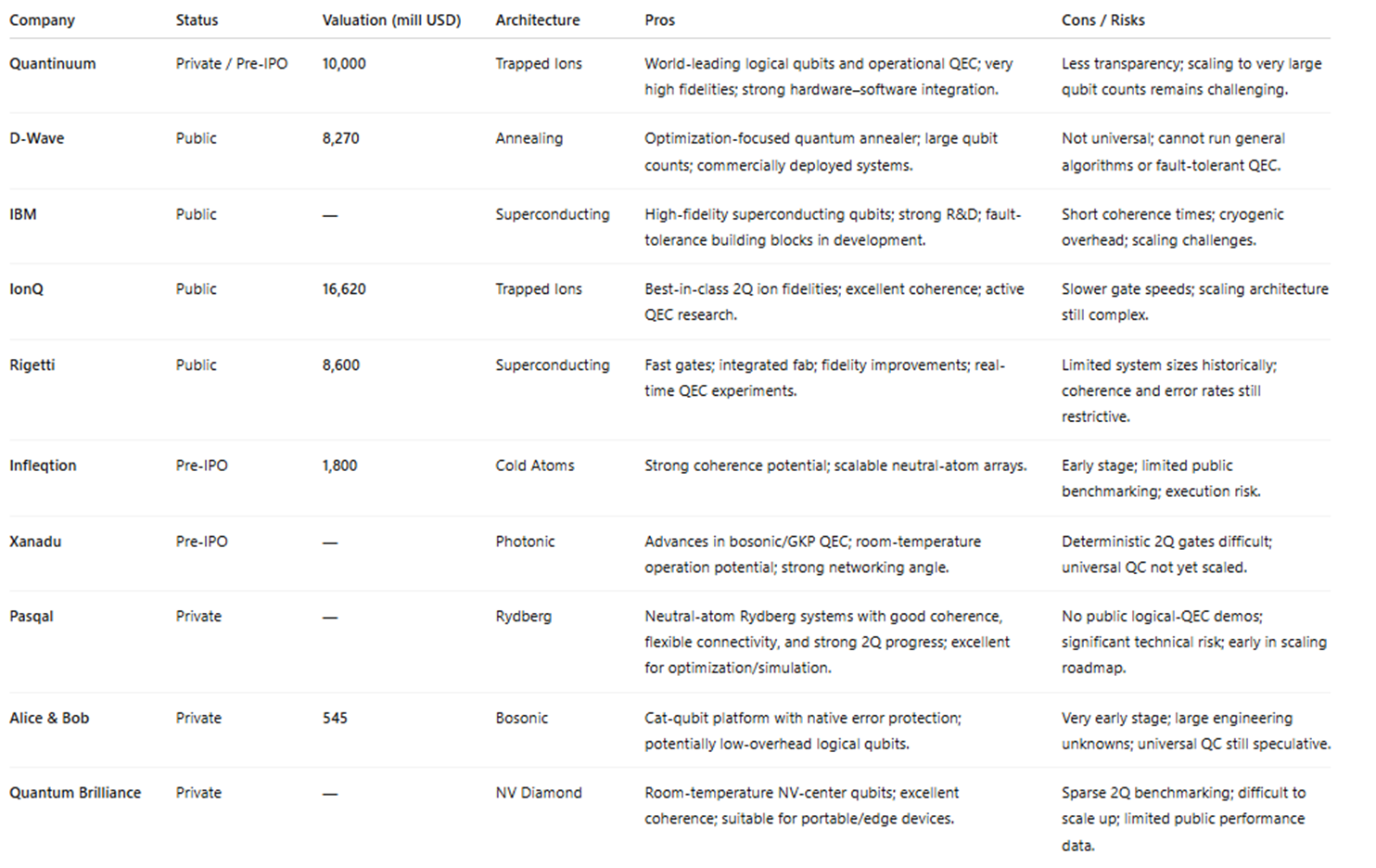
Key Quantum Players 2025
Basic Primer Quantum Terms
- Qubit: the basic unit of quantum information that can exist in a superposition of 0 and 1.
- Superposition: a quantum state where a qubit occupies multiple states simultaneously.
- Entanglement: a correlation between qubits so strong that measuring one instantly constrains the other.
- Quantum Gate: a controlled operation that changes a qubit's state, analogous to a logic gate.
- Gate Speed: how fast a quantum operation is executed on a qubit.
- Gate Fidelity: the accuracy with which a gate performs the intended quantum operation.
- Quantum Circuit: a sequence of quantum gates applied to qubits to perform a computation.
- Quantum Error (QE): Any unwanted change in a qubit's state caused by noise, decoherence, or imperfect control.
Advanced Quantum Computing Terms
- Logic Loader: The compilation layer that maps logical quantum circuits onto physical hardware gates. Handles routing, scheduling, and gate translation under hardware connectivity and noise constraints.
- Quantum Error Correction (QEC): techniques that protect quantum data by encoding it into multiple qubits.
- Operational QEC: Quantum error correction that runs live on hardware, performing real-time syndrome extraction and correction.
Indicates practical, not theoretical, QEC capability.
- Logical Qubits: Error-corrected qubits encoded across many physical qubits to form a stable, long-lived quantum bit. They allow deep circuits and fault-tolerant computation by suppressing physical noise.
- Non-Universal Optimization Capacity: A system that solves or accelerates certain optimization or sampling problems but cannot run general quantum algorithms.
Typical of analog or annealing devices without a universal gate set.
- Fidelities: Measures of accuracy comparing the actual quantum operation or state to the ideal one (0–1 scale). Higher fidelity means fewer errors and better performance.
- 2Q Fidelity (Two-Qubit Fidelities): Accuracy of two-qubit entangling gates such as CZ or CNOT. This is the most critical metric for scalable quantum computing and determines QEC viability.
- CZ Gate (Controlled-Z): A common 2-qubit gates that applies a Z (phase flip) to the target qubit only when the control qubit is in state |1⟩. In layman terms, it applies the rule "If the first qubit is 1, add a phase twist to the second one; otherwise do nothing." or, even more intuitively, "If the control light is ON, the second light stays the same, but its mood flips-its phase changes even though its brightness doesn't."
- CNOT Gate (Controlled-NOT): Another 2-qubit gate that flips (NOTs) the target qubit only when the control qubit is in state |1⟩. In layman terms, it applies the rule "If the first qubit is 1, flip the second one; otherwise do nothing." or, even more intuitively, "If the control light is ON, toggle the second light; if it's OFF, leave it alone."
- Quantum Coherence: How long a qubit maintains its quantum information (phase and superposition). Determined by T₁ (relaxation aka time a qubit keeps its energy ) and T₂ (dephasing aka time a qubit keeps its phase) times.
- Decoherence: Defined as the loss of quantum information due to environmental interactions.
- Cross-Talk: unintended interference between neighboring qubits during operations.
- Readout Error: inaccuracies when measuring the state of a qubit.
- T₁/T₂ 2Q Progress: Improvement in relaxation (T₁) and dephasing (T₂) times and their impact on two-qubit gate performance. Better coherence → faster, cleaner 2Q gates → higher fidelity. Beware T₂ is usually much shorter than T₁ because phase noise from the environment is more damaging than energy relaxation.
- Quantum Transparency: The degree to which a system or medium preserves quantum states without distortion or loss. Used in both communication (photonic loss) and computation (effectively noise-free channels).
- Theory 6: Theoretical quantum error-correction strength equivalent to a code distance of 6. In this way, a code distance of 6 means the quantum error-correcting code can tolerate up to 2 errors (it can correct ⌊(d–1)/2⌋ = 2 errors), and detect up to 5 errors. That said, although the code is theoretically distance 6, real hardware today does not yet reach distance 6 logical performance.
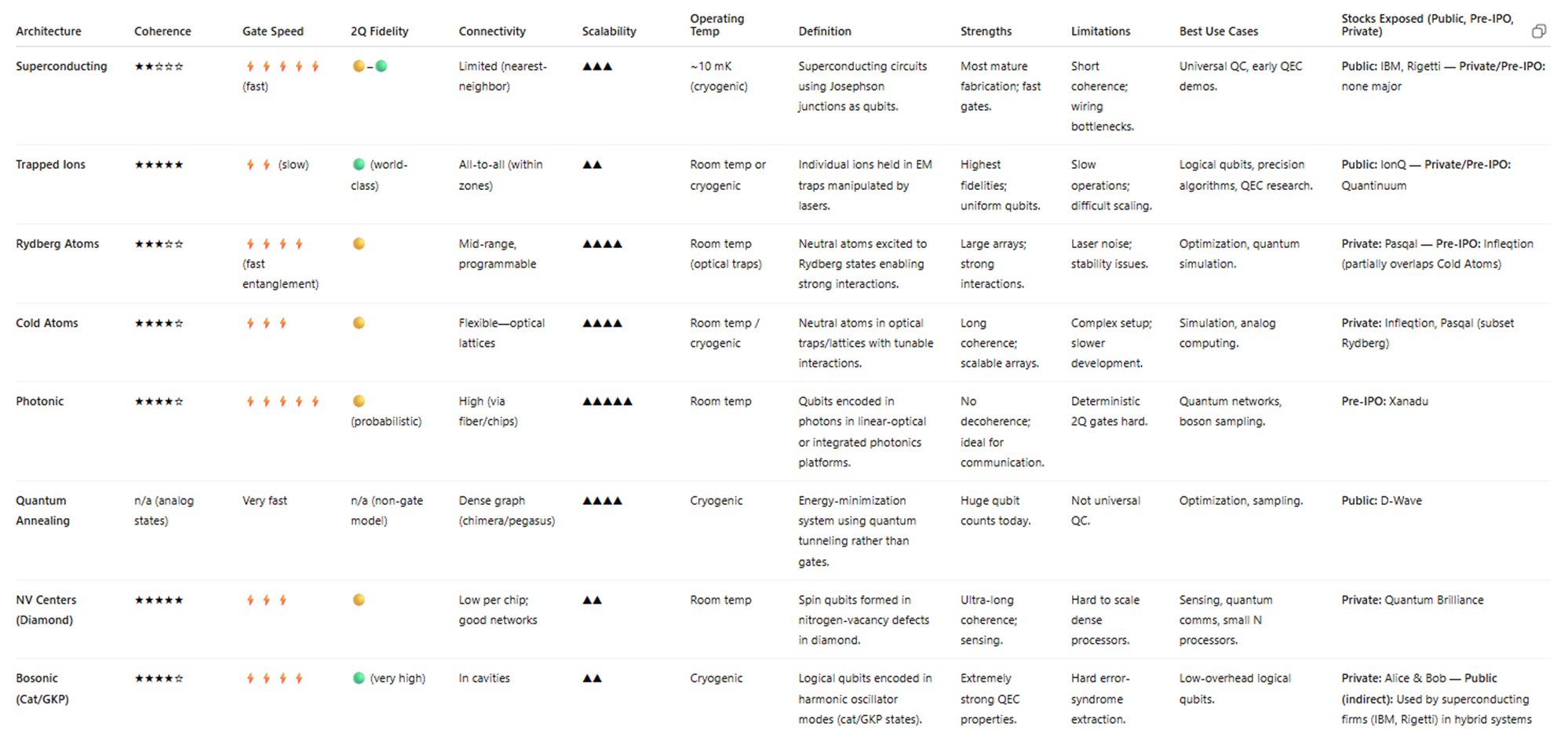
Quantum Architectures Comparison
Note: Feel free to reply to this post adding additional info or correcting any inaccuracies on Quantum breakthroughs or the key players discussed.
------------------------------
Carlos Salas
Portfolio Manager & Freelance Investment Research Consultant
------------------------------